Photogrammetry and LiDAR scanning are two popular techniques used in conjunction with drones for surveying and mapping purposes. Both methods have revolutionised the field of geospatial data collection, offering highly detailed and efficient ways to capture accurate representations of the physical environment. However, while both technologies can be employed to achieve similar goals, they operate on fundamentally different principles, and the choice between them can significantly impact the accuracy, cost, and suitability of the final output.
Understanding the differences between the two methods and knowing when to use each can help optimise data collection and processing for a wide range of applications, from construction and infrastructure planning to environmental monitoring and agricultural management. This article delves into how each technology works, explores their strengths and limitations, and provides guidance on selecting the right approach for your project.
L2 LiDAR scanning paired with drones has revolutionised the way large areas of ground are surveyed, allowing for the efficient generation of detailed point cloud models. In a blog post detailing the benefits of this technology, one could cover several key advantages:
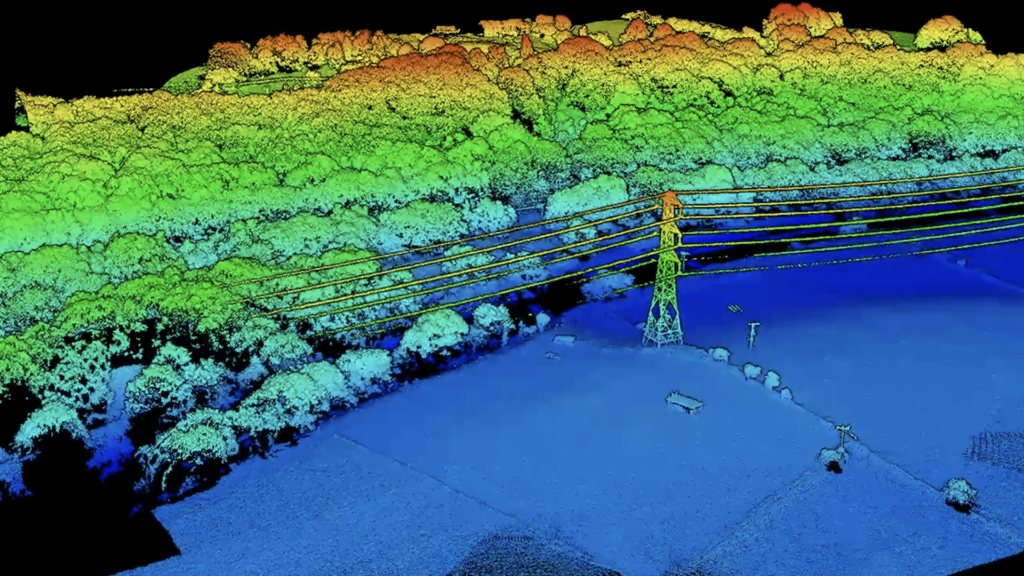
In summary, while both photogrammetry and LiDAR scanning have their strengths and weaknesses, the choice between the two often comes down to the specific requirements of the project, including accuracy needs, budget considerations, and environmental conditions. Understanding these differences can help surveyors and professionals make informed decisions when selecting the most suitable technology for their drone-based surveying tasks.
L2 LiDAR scanning paired with drones has revolutionised the way large areas of ground are surveyed, allowing for the efficient generation of detailed point cloud models. In a blog post detailing the benefits of this technology, one could cover several key advantages:

In summary, while both photogrammetry and LiDAR scanning have their strengths and weaknesses, the choice between the two often comes down to the specific requirements of the project, including accuracy needs, budget considerations, and environmental conditions. Understanding these differences can help surveyors and professionals make informed decisions when selecting the most suitable technology for their drone-based surveying tasks.
Photogrammetry is a widely used surveying technique that leverages images captured from different angles to generate detailed 3D models. When combined with drone technology, photogrammetry provides a cost-effective and efficient solution for projects requiring high-resolution imagery and spatial data.
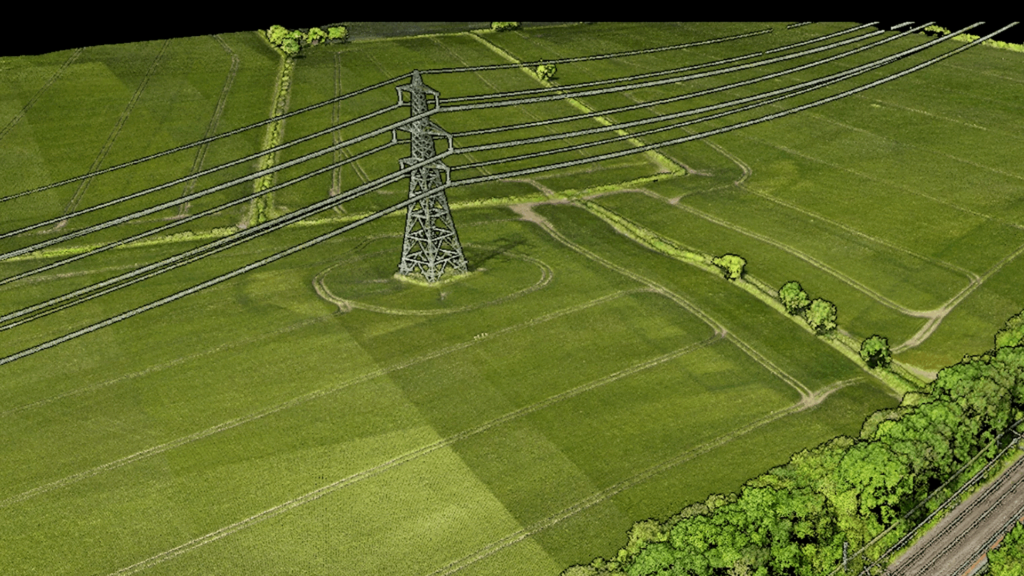

L2 LiDAR scanning paired with drones has revolutionised the way large areas of ground are surveyed, allowing for the efficient generation of detailed point cloud models. In a blog post detailing the benefits of this technology, one could cover several key advantages:

In summary, while both photogrammetry and LiDAR scanning have their strengths and weaknesses, the choice between the two often comes down to the specific requirements of the project, including accuracy needs, budget considerations, and environmental conditions. Understanding these differences can help surveyors and professionals make informed decisions when selecting the most suitable technology for their drone-based surveying tasks.

Matrix Consulting Engineers
The Business Village,
Innovation Way, Barnsley,
S75 1JL
Tel: 0333 014 2926
Email: info@matrixce.co.uk
